
It is a type of substitution cipher For example, with a left shift of 3, D would be replaced by A, E would become B, and so on. DCODEX is coded GFRGHA Encryption 21.5 Alphabet 15.9 Cipher 13.9 Shift key 7.4 Encoder 4.6 Code 4.6 Letter (alphabet) 4.4 Caesar cipher 4.2 Source code 3.9 Bitwise operation 3.7 Substitution cipher 3.6 Cryptography 3.6 Alphabet (formal languages) 3.1 Crypt (Unix) 3.1 D (programming language) 2.8 Mathematics 2.8 Solver 2.8 Modular arithmetic 2.7 X 2.6 Character encoding 2.6Ĭaesar cipher - Wikipedia en./wiki/Caesar_cipherĬaesar cipher - Wikipedia In cryptography, a Caesar cipher Caesar 's cipher Caesar 's code or Caesar m k i shift, is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques.
CAESAR CIPHER TRANSLATOR MOD
To encrypt X=23, 23 3=26 and 26 mod 26 = 0, 0=A, so X is encrypted with A, etc. Example: To crypt D of value 3, add the shift 3: 3 3=6 and find the letter for 6 : 6=G, so D is crypted with G. , Z=25, and add a constant the shift, then the result modulo 26 alphabet length is the coded text. DCODEX is coded GFRGHA Another way to crypt, more mathematical, note A=0, B=1. To encrypt X, loop the alphabet: after X : Y, after Y : Z, after Z : A. To encrypt D, take the alphabet and look 3 letters after: G. Plain Alphabet ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ Caesar Alphabet 3 DEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABC Example: Crypt DCODEX with a shift of 3. The most commonly used shift/offset is by 3 letters.

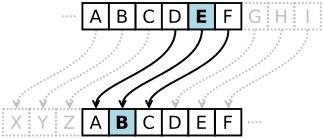
a same letter is replaced with only one other always the same for given cipher n l j message.

Caesar Cipher (Shift) - Online Decoder, Encoder, Solver, Translator G CCaesar Cipher Shift - Online Decoder, Encoder, Solver, Translator Encryption with Caesar w u s code is based on an alphabet shift move of letters further in the alphabet, it is a monoalphabetic substitution cipher S Q O, ie.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
